On-Premises AD DS Authentication for Azure Files
Overview — On-premises Active Directory Domain Services authentication over SMB for Azure file shares
Summary
Azure Files supports identity-based SMB authentication using Kerberos via:
On-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
Microsoft Entra Domain Services
Microsoft Entra Kerberos for hybrid user identities
This article focuses on enabling and configuring on-premises AD DS for Azure file shares.
Recommended reading: the How it works section (link in source) and the Azure Files planning guide (link in source).
Supported scenarios and restrictions
Share-level RBAC required for identity-based authentication:
Default share-level permission: applies RBAC to all authenticated identities (no AD-to-Entra sync required).
Granular share-level permissions: requires the corresponding on-premises AD DS identities to be synced to Microsoft Entra ID via Microsoft Entra Connect.
Note: groups created only in Microsoft Entra ID won't work unless they contain synced user accounts. Password hash sync is not required.
Client OS requirements: Windows 8 / Windows Server 2012+, or Linux VMs (Ubuntu 18.04+, equivalent RHEL/SLES).
Kerberos uses AES 256 encryption (recommended). AES 128 is not supported.
Single sign-on (SSO) is supported.
By default access is limited to the AD forest where the storage account is registered; other forests require configuring a forest trust.
Identity-based authentication is not supported for NFS file shares.
AD DS can be hosted on-premises or in an Azure VM.
Prerequisites (high level)
Have an AD DS environment and sync it to Microsoft Entra ID using Microsoft Entra Connect, unless you plan to rely on default share-level permission.
Domain-join client machines (on-prem or Azure VMs) to the AD DS domain. Non-domain-joined machines can still authenticate if they have network access to the domain controllers and explicit credentials are provided.
Create or select an Azure storage account (same subscription/tenant as Entra tenant). Ensure the storage account isn’t already configured with another identity source — disable it first if it is.
If you plan networking restrictions on the share, complete networking configuration beforehand.
Overview of how it works
Sync on-prem AD DS identities to Microsoft Entra ID via Microsoft Entra Connect.
Assign share-level RBAC to the synced Microsoft Entra identity (or use default share-level permission).
Manage file/directory access via Windows ACLs (DACLs are preserved and enforced).
AD DS-joined machines can mount Azure file shares using existing AD credentials for SSO.
This enables lift-and-shift of on-prem file servers with minimal credential changes for users.
Setup (high-level steps)
Diagram
End-to-end workflow diagram (as in original):
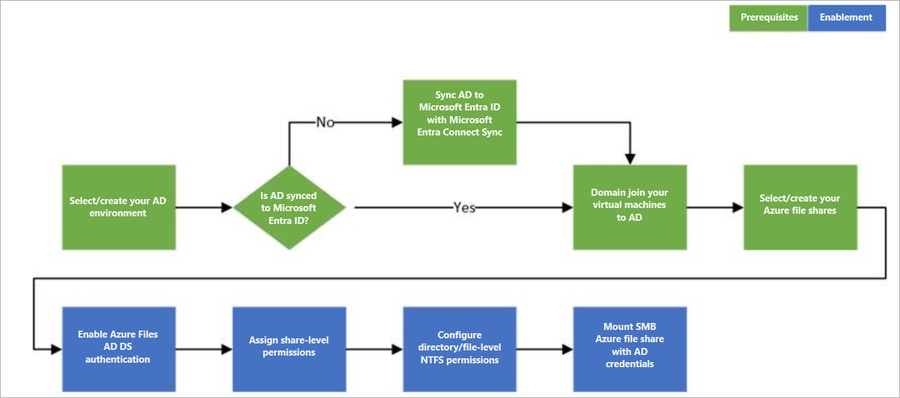
Next step
To get started: enable AD DS authentication for your storage account (link preserved in original).
Additional notes
Ensure Microsoft Entra tenant and storage account share the same subscription.
If you encounter mounting issues, refer to the troubleshooting guidance referenced in the original article.
Last updated in source: 12/26/2025
(Links and images kept exactly as in the original article.)
Was this helpful?